Cordova Plugin Generator
The Problem
The other day i was looking to create a plugin to use with my Apache Cordova app. While there is nice documentation about how to create and then use that plugin, there was no way to generate one from a tool( cordova-cli/plugman/yeoman ).
So in the spirit of Open Source, i decided to embark on a quest, er, i mean, i decided to create something that would quickly scaffold a basic Cordova plugin.
Start
I decided to go with yeoman, since i was curious how their generators worked.
But the cordova team has created cordova-cli and plugman. These tools allow you to manage the plugins you use in a cordova project, but they didn’t yet have plugin creation. Since plugin creation should really be in these tools, i deciced to fork plugman, which is what is used under the hood in cordova-cli, and create a branch that i’ll use for my yeoman generator and possibly be added to the upstream project.
Yeoman would just call these new plugman api’s. And since the api’s are still in flux, adding the abstraction layer of yeoman will help the user a bit.
The Start of a Solution
Plugman allows you to easily manage your Cordova applications plugins with a fun api for node and the CLI.
It’s easy to install
$ npm install -g plugman
then i if you want to install a plugin, you can execute this command( or something similar ):
$ plugman --platform ios --project ~/project/CordovaProject --plugin ~/SuperCoolPlugin
You can also install plugins from remote repo’s such as git or http
Also, you can specify multiple --variable name=value arguments depending if your plugin needs that sort of thing.
Plugman also allows you to unistall, publish/search/unpublish a plugin to a plugin repo.
The one thing that is missing is the ability to actually scaffold out a plugin.
Thats where i decided to start.
Step 1.
The Heart of any plugin is the plugin.xml file. There is a plugin.xml spec here
I really dislike xml, but what are you going to do
This specifies the plugins name, and id, and the version number. There are some other optional fields like descripiton and author that can be entered also.
So i set out to have this first command just create this file with the basic things as well as setup up a little folder structure similiar to this
Now since i’m on my fork, and none of this has been upstreamed yet, these method names are subject to change.
Here is my fork
Make sure to checkout the for_yeoman branch!!
I decided to name the first command create.
There are 3 required parameters
-
name
This will be the name of the plugin
-
plugin_id
The id of the plugin, example: org.cool.plugin
-
plugin_version
The plugin version, example: 0.0.1
You can also pass multiple variable arguments. These will be added to the plugin.xml as children of the main plugin tag
so you can execute like this:
$ plugman create --name Super --plugin_id "org.super.cool" --plugin_version 0.0.0 --variable description="Awesome PLugin"
This would result in the following plugin.xml created
<plugin id="org.super.cool"
version="0.0.1"
xmlns="http://apache.org/cordova/ns/plugins/1.0"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<name>Super</name>
<description>Awesome PLugin</description>
<js-module name="Super" src="www/Super.js">
<clobbers target="cordova.Super"/>
</js-module>
</plugin>
You will also notice that a src/ and www/ folder were also created along with a basic JS template for a plugin
var cordova = require('cordova'),
exec = require('cordova/exec');
var Super = function() {
this.options = {};
};
Super.prototype = {
/*
Add your plugin methods here
*/
coolMethod: function( args, success, error ) {
cordova.exec( success, error, "Super", "coolMethod", args );
}
};
var SuperInstance = new Super();
module.exports = SuperInstance;
Thats cool!!
But now how to add a platform?
Step 2.
The next command i added is platform
I’m not really thrilled by this, but for now i think it will work.
so:
$ plugman platform --platform_name=ios
This will add the <platform> tags to the plugin.xml as well as create an ios/ source folder in src/
Also in the ios/ source folder, A basic .h and .m file will be created.
So here is the plugin.xml after these commands:
<plugin id="org.super.cool"
version="0.0.1"
xmlns="http://apache.org/cordova/ns/plugins/1.0"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<name>Super</name>
<js-module name="Super" src="www/Super.js">
<clobbers target="cordova.Super"/>
</js-module>
<platform name="ios">
<config-file parent="/*" target="config.xml">
<feature name="Super">
<param name="ios-package" value="CDVSuper"/>
</feature>
</config-file>
<header-file src="src/ios/CDVSuper.h"/>
<source-file src="src/ios/CDVSuper.m"/>
<framework src="MobileCoreServices.framework"/>
</platform>
</plugin>
And the contents of your src/ios folder are now
/********* CDVSuper.h Cordova Plugin Header *******/
#import <Cordova/CDV.h>
@interface CDVSuper : CDVPlugin
- (void)coolMethod:(CDVInvokedUrlCommand*)command;
@end
/********* CDVSuper.m Cordova Plugin Implementation *******/
#import "CDVSuper.h"
#import <Cordova/CDV.h>
@implementation CDVSuper
- (void)coolMethod:(CDVInvokedUrlCommand*)command
{
CDVPluginResult* pluginResult = nil;
NSString* echo = [command.arguments objectAtIndex:0];
if (echo != nil && [echo length] > 0) {
pluginResult = [CDVPluginResult resultWithStatus:CDVCommandStatus_OK messageAsString:echo];
} else {
pluginResult = [CDVPluginResult resultWithStatus:CDVCommandStatus_ERROR];
}
[self.commandDelegate sendPluginResult:pluginResult callbackId:command.callbackId];
}
@end
So in theory once other platforms have been added to plugman, you could then do
$ plugman platform --platform_name=android
To add the android specific stuff.
This allows for progressive enhancement.
Step 3 - Yeoman
So, good. For a first start that works not bad. Now it’s time to put a front end on it. That is where yeoman comes in.
Instead of using the CLI to call plugman, you can also get access to the api in a node.js environment.
So using as a wrapper, we can construct a little user friendly front end.
I’m not going to go into the workings of a yeoman generator, but just on what the front end will look like.
First we need to install the generator:
$ npm install -g generator-cordova-plugin
Now that we have that installed, lets first create a directory to create our plugin in and then cd into it.
$ mkdir coolPluginDirectory
$ cd coolPluginDirectory
Now we can run the yo command:
$ yo cordova-plugin
If things went ok, we should see this screen:
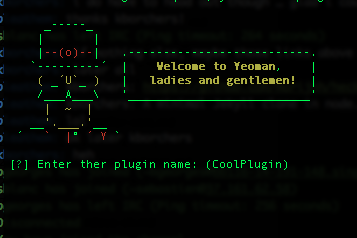
Now just follow the bouncy ball. Note: there isn’t actually a bouncing ball
If all goes successfully, you will have something similar to what you got when running the plugman create command
to run the next command make sure you are in the directory that was just created, then do this:
$ yo cordova:platform add
You will see this screen:
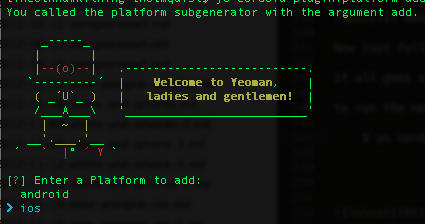
choose ios
Again, you should have something similar to running the plugman platform command
End
While there is still much to be done, this will atleast help get started a little bit quicker when trying to create Cordova Plugins